A winemaker has many options for vessels to ferment and age wine in. While you’re probably familiar with stainless steel tanks and oak barrels, you might not know about amphorae – large, egg-shaped clay vessels – that are growing in popularity in recent years. While it might seem a trendy new thing, amphorae-ageing is in fact a practice that dates back thousands of years. Let’s find out what they’re all about.
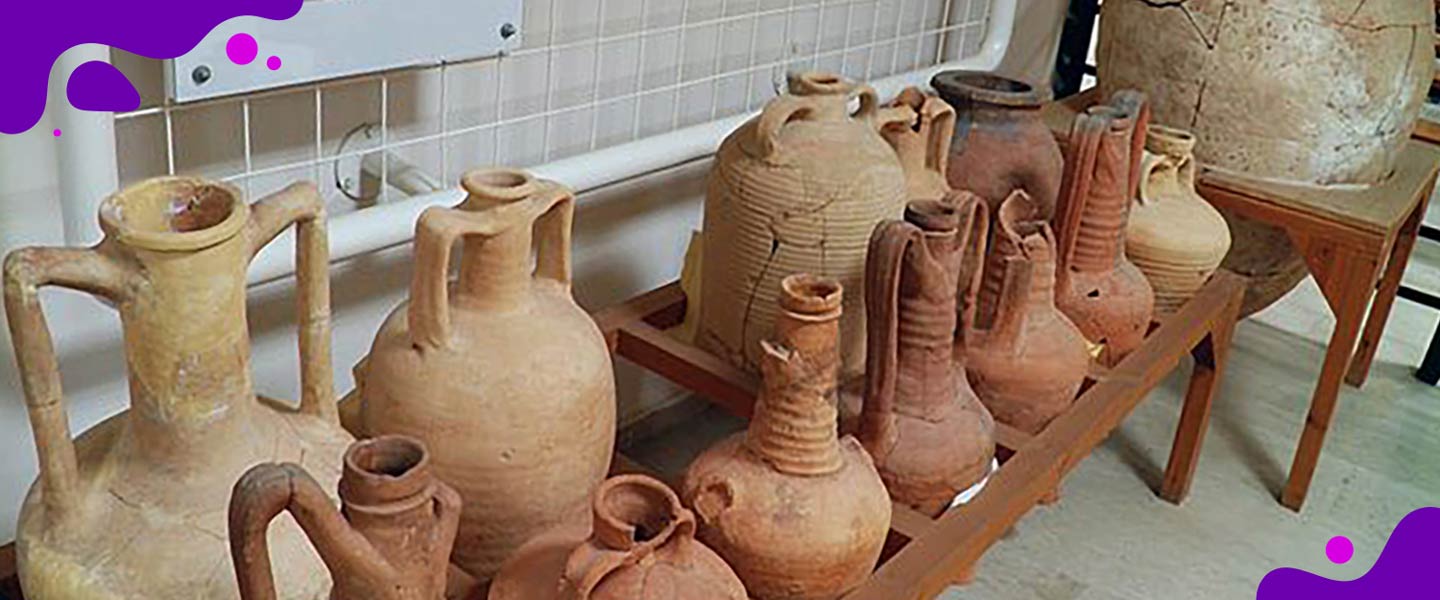

Amphorae: What are They?
It is believed that winemaking has its roots in the South Caucasus, known as the Republic of Georgia today. Archaeologists have found seeds of grapes and remnants of clay pots dating back more than 8,000 years. Ancient Georgians used the clay vessels, called ‘qvevri’, to ferment and store wine in. The vessels were usually buried in the ground up to the neck. This was to keep a consistent temperature while the wine fermented.
During the Bronze and Iron ages, amphorae spread across the Mediterranean. They served the Greeks and Romans as a means of transporting and storing wine, olive oil, grains, and other foods.
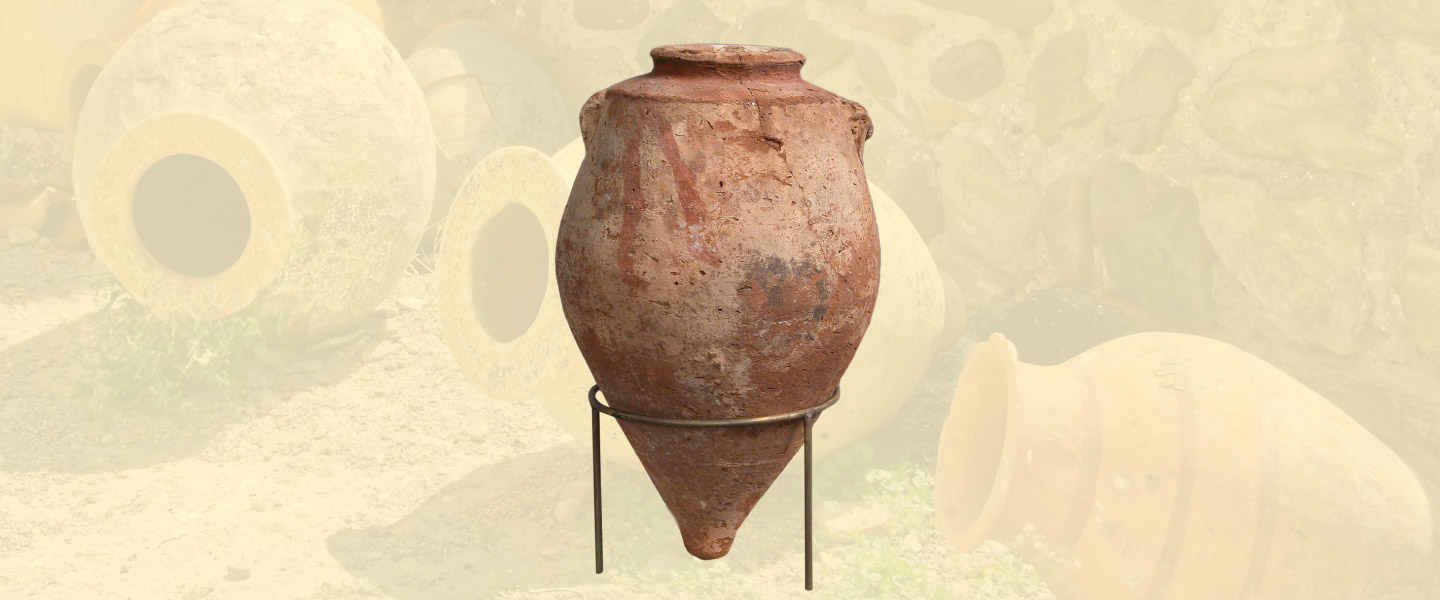

Different types of amphorae were used for different purposes. Amphorae used for fermentation were similar to qvevri. These were quite large, and rounded. Buried underground during primary fermentation, the wine would be transferred to smaller amphorae. This was important for transportation and ageing, and smaller amphorae such as the Roman amphorae were used.
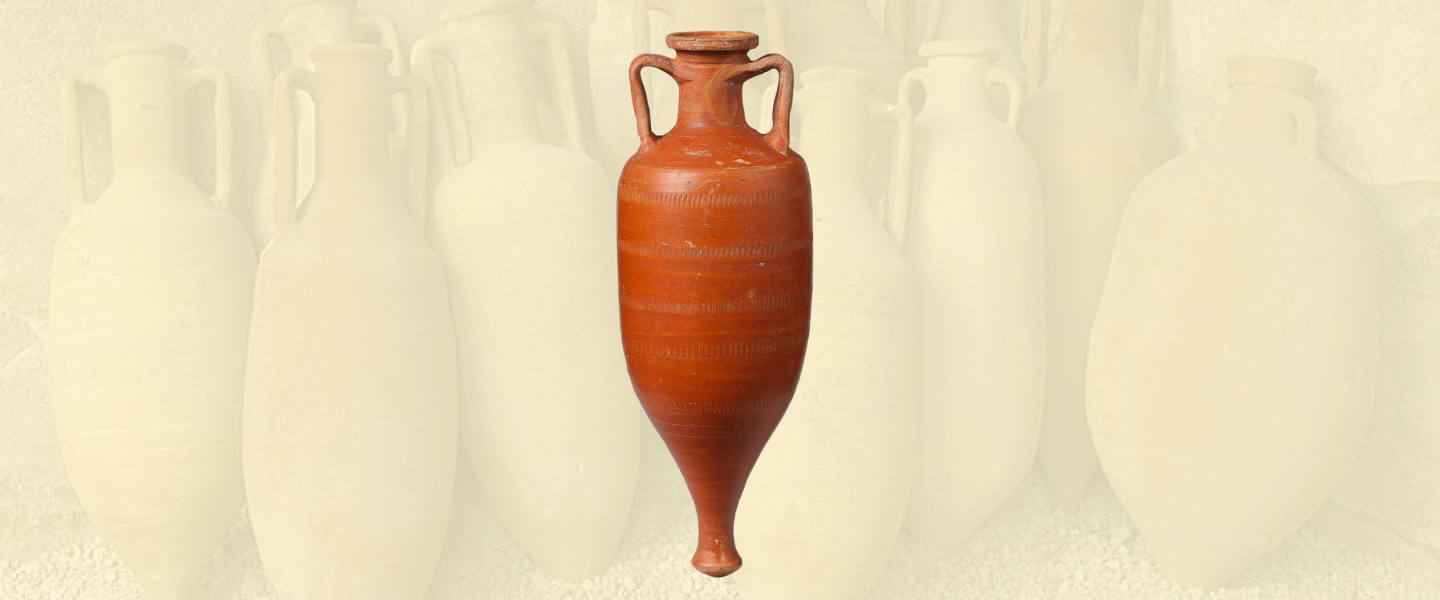

Roman amphorae were slender and smaller than their qvevri counterparts. They had slender necks with large handles on their sides to assist with transportation. Another characteristic that stood out were their long and pointed bottoms. These assisted in stacking them, since the bottom of the amphorae would fit into the space between the amphorae necks.
Why are Amphorae Making a Comeback?
Modern winemakers in Georgia were the first to re-embrace their qvevri roots. The practice of fermenting and ageing wine in amphorae was then adopted by a few Northern Italian winemakers who were interested in making minimal-intervention wines. Today, amphorae have spread to winemaking regions across the globe and are no longer only used by natural winemakers. It’s important to note that the practice isn’t adopted on a massive scale or used for mass-produced wines, but it’s becoming more and more common for quality winemaking. Why?
Most importantly, clay (which amphorae are made of) is porous. This porosity allows for microoxygenation to occur within the vessel, aiding in the softening of tannins, and ultimately the development of a more supple and delicious wine.
Secondly, amphorae keep a stable and cool temperature and (due to their clay composition) are neutral in flavour, so it does not impart any flavours like oak does. This allows the wine to slowly evolve, aiding in the creation of fresh and fruity aromas.
Lastly, the shape of the amphora allows for movement of particles within the wine. The rounded shape is especially important, because there are no corners for wine to collect in. This creates a constant suspension where the wine is in contact with the skins that float on the surface. The shape also allows for the yeast lees and sediment to sink to the bottom of the vessel.
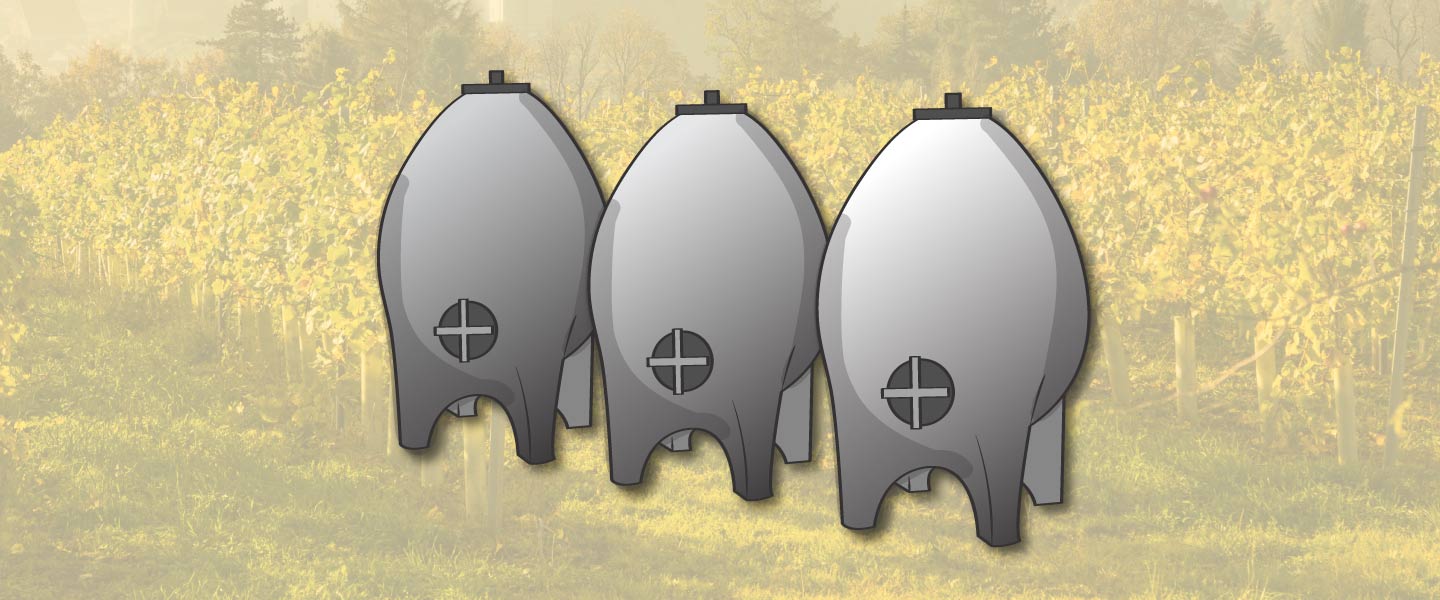

Wine Eggs: What are they?
Now that you know what amphorae are, do you think you can guess what a wine egg is?
You guessed it! Eggs are another type of vessel used for ageing wine. They are made from concrete, oak or stainless steel instead of clay and yes, they look like giant eggs. While the use of concrete vessels to age wines does go back a few thousand years as well, it wasn’t until 2001 that the first modern concrete wine egg was made.
Tradition to Trend
In 2001 Michel Chapoutier, a winemaker pioneering in biodynamic viticulture, collaborated with Nomblot, a French company specializing in creating concrete wine containers. Together, they produced the first modern egg-shaped wine fermenter out of concrete, and from there the popularity rose as Nomblot continued to create these fermenters for other wineries.
Why Are Wine Eggs a Popular Choice?
Similar to the amphora’s, the egg’s properties led to its popularity in the winemaking world.
A concrete egg does not impart any aromas or flavours to the wine in the way that oak does. The concrete provides a neutral vessel for wine to age and develop in, allowing the fruit and terroir to shine within the wine.
Secondly, similar to clay, concrete is porous and provides the opportunity for microoxygenation to occur in the wine. Similar to how a cork lets oxygen in, the concrete pores allow for small amounts of oxygen to enter the egg, softening the tannins and making the wine more plush. This process happens much faster in concrete than it would in stainless steel eggs or barrels.
And lastly, the shape! The large egg shape allows for a similar current or vortex to form within the egg like it does in the amphorae. As yeast ferments the wine and increases its temperature, the (already fermented) wine would rise to the top, and the cooler wine sinks to the bottom of the vessel. This allows the wine to circulate throughout the vessel without the need to stir it.
Concrete and Clay Versus Steel and Oak
It’s likely that concrete and clay are not here to replace stainless steel and oak, there is a change coming as winemakers bring back traditional winemaking practices back in some of their vintages.
If you’re interested in learning more about wines that are aged and fermented in amphorae and wine eggs, check out wineries like Tenuta Casadei, Chapoutier Winery or even Beckham Estate vineyard that use traditional vessels to ferment their wine.
And if you’re looking for some unique, tasty and world-renowned wines, be sure to check out our WineCollective member store where you’ll save up to 50% off retail pricing! If you’re not a member yet, what are you waiting for? Sign up for a “no-strings attached” membership that gets you great wine, wine education, recipes, pairings, and other member perks!